Idea Validation Cheat Sheet: Know if Your Idea Will Make Money Before You Start
Dairrick Anthony Jordan • 2024-08-13
Don’t waste time on a dud—use this cheat sheet to quickly and effectively validate your idea’s income potential before you invest your time and energy.
Don’t waste time on a dud—use this cheat sheet to quickly and effectively validate your idea’s income potential before you invest your time and energy.
Hey there, savvy entrepreneur!
Before you dive headfirst into executing that brilliant idea of yours, you need to ask yourself a crucial question:
Will this idea make money?
The reality is, not every idea is worth pursuing—at least not in its current form. That’s where validation comes in. By answering a few key questions and using some proven criteria, you can determine whether your idea has the potential to generate income, or if it needs a bit more refinement.
This Idea Validation Cheat Sheet is designed to be your go-to resource for quickly assessing your idea’s viability. No fluff, just actionable steps to help you make an informed decision.
Let’s get started!
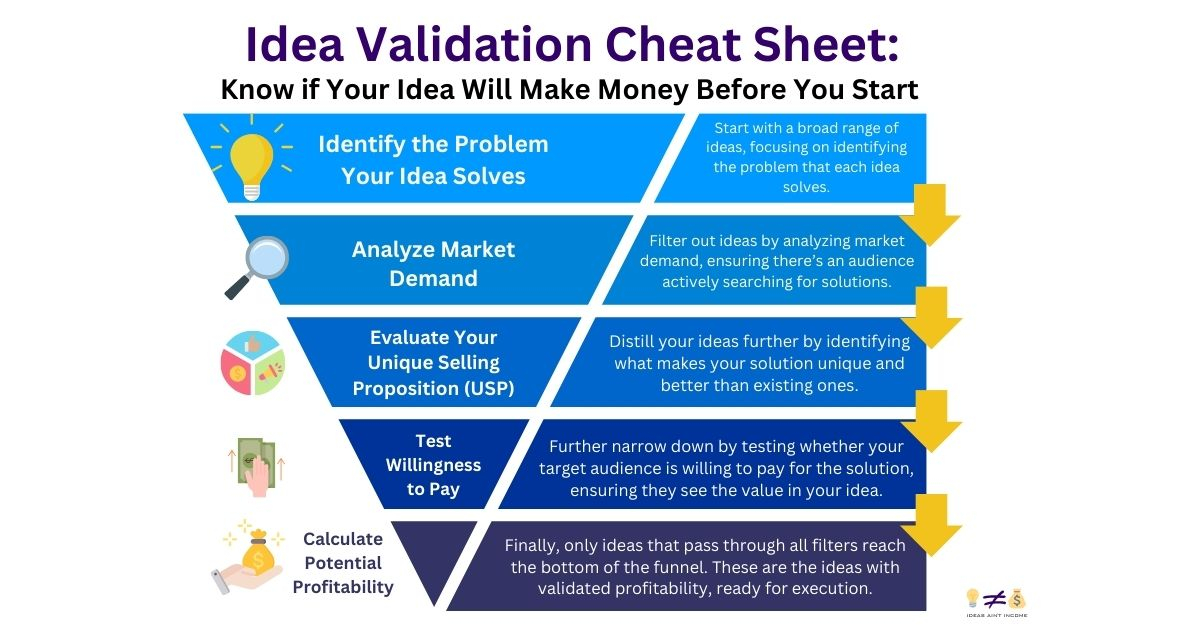
Step 1: Identify the Problem Your Idea Solves
Every profitable idea solves a problem. The bigger the problem, the more willing people are to pay for a solution. If your idea doesn’t address a specific pain point or need, it’s unlikely to generate significant income.
🔑 Key Questions to Ask:
- What problem does my idea solve?
- Who experiences this problem most acutely?
- How does my solution improve their current situation?
▶️ Step-by-Step Instruction:
- Define the Problem: Write down the specific problem your idea addresses. Be as clear and specific as possible.
- Example: “Freelancers struggle to find high-paying clients consistently.”
- Target Audience: Identify who has this problem and who would be willing to pay for a solution.
- Example: “Freelancers who are tired of low-paying gigs and want to increase their income.”
- Value Proposition: Describe how your idea offers a better or unique solution to this problem compared to what’s currently available.
- Example: “My idea is a course that teaches freelancers how to market themselves effectively and land high-paying clients.”
🏃 Exercise:
Create a “Problem-Solution Statement” that clearly articulates the problem your idea solves and the benefit it provides. This will serve as the foundation for the rest of your validation process.
NoCo, LoCo Resource Recommendation:
- AnswerThePublic: Use this free tool to discover the most common questions and problems your target audience is searching for. This will help you refine your problem statement.
Step 2: Analyze Market Demand
High-Value Insight:
Even if your idea solves a significant problem, there must be enough demand for that solution. Market demand is a key indicator of whether your idea has income potential. If there’s no demand, it doesn’t matter how great your idea is—it won’t make money.
🔑 Key Questions to Ask:
- Are people already searching for solutions to this problem?
- Is the market growing, stable, or declining?
- What’s the competition like?
▶️ Step-by-Step Instruction:
- Search Volume Analysis: Use keyword research tools to determine how many people are searching for solutions related to your idea.
- Example: “Research keywords like ‘how to find high-paying clients’ to see how many people are searching for this topic.”
- Market Trends: Look at industry reports and trends to see if the market for your idea is growing or shrinking.
- Example: “Freelancing and gig economy reports show a growing trend, indicating increasing demand for freelance-related solutions.”
- Competitive Landscape: Identify existing products or services that solve the same problem. Analyze their success to gauge market demand.
- Example: “Identify popular online courses, tools, or books that teach freelancers how to find better clients.”
Exercise:
🏃 Exercise:
Conduct a quick market demand assessment using Google Trends. Search for keywords related to your idea and note whether interest is increasing, stable, or declining.
NoCo, LoCo Resource Recommendation:
- Google Trends: Use this tool to analyze the popularity of search terms over time and get a sense of market demand.
Step 3: Evaluate Your Unique Selling Proposition (USP)
Your idea needs to stand out in the marketplace. A strong Unique Selling Proposition (USP) differentiates your idea from the competition and makes it more attractive to your target audience.
🔑 Key Questions to Ask:
- What makes my idea different from existing solutions?
- Why would someone choose my solution over others?
- What unique benefits do I offer?
▶️ Step-by-Step Instruction:
- Identify Gaps: Look at existing solutions and identify what they’re missing or where they fall short. This is where your idea can fill the gap.
- Example: “Most freelance courses focus on basic skills, but few offer advanced marketing techniques. My course will focus on high-level client acquisition strategies.”
- Highlight Uniqueness: Pinpoint the aspects of your idea that are unique, whether it’s the approach, features, or delivery.
- Example: “My course includes personalized feedback and live coaching sessions, which competitors do not offer.”
- Craft Your USP: Write a clear, concise statement that communicates what sets your idea apart and why it’s the best solution for your target audience.
- Example: “The only freelancing course that teaches advanced marketing techniques and includes personalized live coaching.”
🏃 Exercise:
Create a comparison chart that highlights the differences between your idea and the top three competitors. Use this to refine your USP.
NoCo, LoCo Resource Recommendation:
- Canva: Use this free tool to design a simple comparison chart that visually showcases your USP against competitors.
Step 4: Test Willingness to Pay
It’s not enough for people to like your idea—they need to be willing to pay for it. Testing willingness to pay ensures that your idea has real income potential, not just theoretical interest.
🔑 Key Questions to Ask:
- Would my target audience pay for this solution?
- How much would they be willing to pay?
- What pricing model works best for my idea?
▶️ Step-by-Step Instruction:
- Pre-Sell Your Idea: Before fully developing your idea, offer a pre-sale to gauge interest and willingness to pay. This could be a discounted price or early access.
- Example: “Offer a pre-sale for your course with a limited-time discount to see how many people are willing to buy before it launches.”
- Survey Your Audience: Create a simple survey asking potential customers how much they’d be willing to pay for your solution and what features they value most.
- Example: “Survey your email list or social media followers with questions like, ‘How much would you pay for a course that helps you find high-paying clients?’”
- Analyze Feedback: Use the feedback from pre-sales and surveys to refine your pricing and features. If people are hesitant to buy, find out why and adjust accordingly.
- Example: “If feedback suggests the price is too high, consider offering a payment plan or reducing features to lower costs.”
🏃 Exercise:
Run a pre-sale campaign using your email list or social media following. Track the number of sales and gather feedback on pricing and features.
NoCo, LoCo Resource Recommendation:
- Google Forms: Create and distribute surveys to your audience to collect data on willingness to pay and desired features.
Step 5: Calculate Potential Profitability
High-Value Insight:
Even if your idea has demand and people are willing to pay, you need to ensure it’s profitable. Calculating potential profitability helps you understand whether your idea is financially viable.
🔑 Key Questions to Ask:
- What are my costs to develop and deliver this idea?
- What is my pricing strategy, and how does it impact profitability?
- How many sales do I need to break even and then profit?
▶️ Step-by-Step Instruction:
- Identify Costs: List all costs associated with developing and delivering your idea. This includes production, marketing, distribution, and any ongoing expenses.
- Example: “For a course, costs might include video production, hosting, marketing, and platform fees.”
- Set Pricing: Based on your willingness-to-pay research, set a price for your product or service. Ensure it covers your costs and allows for a profit margin.
- Example: “If your course costs $1,000 to produce, and you price it at $200 per sale, you’ll need to sell 5 courses to break even.”
- Estimate Sales: Determine how many units you need to sell to cover costs and achieve your income goals. Use realistic estimates based on your audience size and marketing reach.
- Example: “To make a profit of $5,000, you’ll need to sell 30 courses at $200 each.”
🏃 Exercise:
Create a simple profitability calculator using a spreadsheet. Input your costs, pricing, and sales estimates to see how profitable your idea can be.
NoCo, LoCo Resource Recommendation:
- Google Sheets: Use this free tool to create a profitability calculator that tracks costs, pricing, and projected sales.
By following this Idea Validation Cheat Sheet, you’ll have a clear, data-driven understanding of whether your idea has the potential to make money. This process not only saves you time and resources but also gives you the confidence to move forward with the right ideas and pivot or refine the ones that need more work.
Validation isn’t a one-time event—it’s an ongoing process that helps you stay aligned with your market and audience. Keep refining, keep testing, and keep moving forward.
Ready to take your validated idea to the next level? Subscribe to "Income Igniter" and get weekly strategies to execute and monetize your ideas, turning them into profitable ventures. No fluff, just actionable insights.